- Arithmetic Logic Unit [ALU]
- Control Unit [CU]
- Register
- Megahertz (MHz):
- a measure of frequency equivalent to 1 million cycles per second.
- Gigahertz (GHz):
- a billion cycles per second.
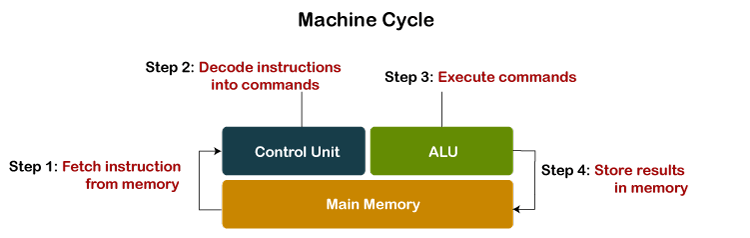
The central processing unit is the most important component of the microcomputer.
It is the electronic brain of the computer.
In addition to processing data, it controls the functions of all the other components.
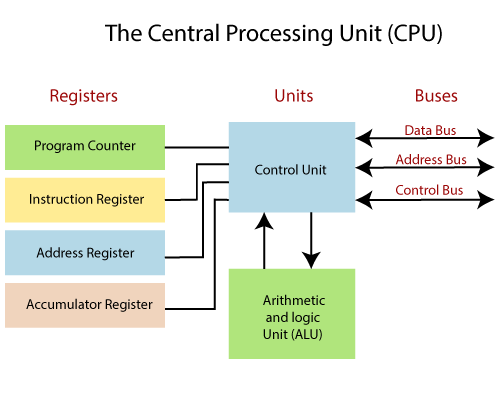
The Central Processing Unit [CPU] or the 'Central Processor' carries out a variety of essential data manipulation [including arithmetic/ logical calculations, comparisons, sorting, etc] and controlling tasks in the computer. CPU consists of
| Memory Unit Table | |
|---|---|
| 1 Bit [Binary digit] | 0 or 1 |
| 1 Byte | 8 Bits |
| 1 Kilo Byte [KB] | 2¹⁰ / 1024 Byte |
| 1 Mega Byte [MB] | 1024 Kilo Byte |
| 1 Giga Byte [GB] | 1024 Mega Byte |
| 1 Tera Byte [TB] | 1024 Giga Byte |
| 1 Peta Byte [PB] | 1024 Tera Byte |
Every microprocessor contains a system clock. The speed at which the processor executes instructions is known as Clock Speed and it is measured in Megahertz (MHz).
Where mega means millions and Hertz means cycles.
Therefore 550 MHz processor performs 550 million cycles per second.
Generally, clock speed determines the system performance.
Technology advances for higher clock speed.
The latest generation of processors operates in gigahertz (GHz)
i.e. a billion cycles per second.
Arithmetic Logic Unit [ALU]
The Arithmetic Logic Unit carries out as the name suggests Arithmetic and Logical operations on the data made available to it.
Basic Arithmetic functions which an ALU can carry out are addition and subtraction.
More powerful CPUs can support additional mathematical operations like multiplication and division.
The logical operation which it can carry out are greater than, equal to, less than and comparison between two numbers.
Besides these operations some processors also support operations which check if particular bits are on or off.
A computer performs its operation in a fraction of a second.
The increasing speeds given below are:
| Millisecond | = | 10⁻³ second |
| Microsecond | = | 10⁻⁶ second |
| Nanosecond | = | 10⁻⁹ second |
| Picosecond | = | 10⁻¹² second |
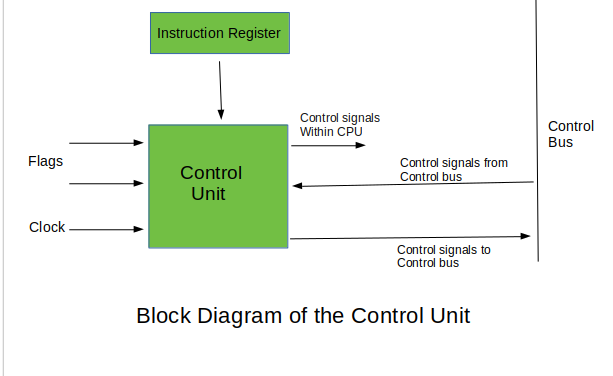
Control Unit [CU]
The Control Unit can be thought of as the brain of the CPU itself.
It controls the computer based on the instructions it decodes, how other parts of the CPU and in turn, the rest of the computer systems should work in order that the instruction gets executed in a correct manner.
Register
The register is a special, high-speed storage area within the CPU.
All data must be represented in a register before it can be processed.
For example, if two numbers are to be multiplied, both numbers must be in registers, and the result is also placed in a register.
The register can contain the address of a memory location where data is stored rather than the actual data itself.
-
The Role of different Registers used in Vnn Neumann model:
- Instruction Register:
- 🔯 IR is used to hold the instruction that is currently being executed.
🔯 The contents of IR are available to the control unit, which generate the timing signals that control the various processing elements involved in executing the instruction.
🔯 Number of bits = 16 - Program Counter:
- 🔯 PC is one of the most important registers in the CPU.
🔯 A program is a series of instructions stored in the memory.
🔯 These instructions tell the CPU exactly how to get the desired result.
🔯 It is important that these instructions must be executed in a proper order to get the correct result.
🔯 This sequence of instruction execution is monitored by the program counter.
🔯 It keeps track of which instruction is being executed and what the next instruction will be.
🔯 Number of bits = 12 - Stack Pointer :
- 🔯 SP is used to point to the top activation record on the run-time stack.
🔯 The run-time stack contains one activation record for each function or procedure invocation that is currently unfinished in the program.
🔯 The top activation record corresponds to the current function invocation.
🔯 When a function call is made an activation record is pushed onto the run-time stack.
🔯 When a function returns, the activation record is popped by decrementing the stack pointer to point to the previous activation record. - Accumulator :
- 🔯 AC is one of the general purpose registers but it is specifically used to 'accumulate' the result of the currently running instructions.
🔯 Number of bits = 16 - Memory Address Register :
- 🔯 MAR are used to handle the data transfer between the main memory and the processor.
The MAR holds the address of the main memory to or from which data is to be transferred.
🔯 Number of bits = 12 - Memory Buffer Register / Memory Data Register :
- 🔯 MBR/MDR are used to handle the data transfer between the main memory and the processor.
🔯 The MDR contains the data to be written into or read from the addressed word of the main memory.
🔯 Number of bits = 16 - Temporary Register :
- 🔯 TR holds temporary data.
🔯 Number of bits = 16 - Input Register :
- 🔯 INPR carries input character.
🔯 Number of bits = 8 - Output Register :
- 🔯 OUTR carries output character.
🔯 Number of bits = 8