An Operating System (OS) is a system software which serves as an interface between a user and a computer.
This controls input, output and other peripheral devices such as disk drives, printers and electronic gadgets.
When a computer is switched on, the operating system is loaded in to the memory automatically. Without an Operating System, a computer cannot effectively manage all the resources.
It is the most important software in a computer system. It consists of the essential files that the computer needs to function.
The following are few uses of Operating System. The main use of Operating System is :
- 🔥 to ensure that a computer can be used to extract what the user wants it do.
- 🔥 Easy interaction between the users and computers.
- 🔥 Starting computer operation automatically when power is turned on (Booting).
- 🔥 Controlling Input and Output Devices.
- 🔥 Manage the utilisation of main memory.
- 🔥 Providing security to user programs.
An operating system that supports only one user at a time

- MS-DOS
- Windows 3x
- Windows 95
- Windows 97
- Windows 98
- Symbian OS
An operating system that allows multiple users to access a computer’s resources at the same time. In such a system a server and terminals are used. In the diagram below, USER-1 acts as the server.
SERVER
a server is a computer that provides data to other computers
TERMINAL
a terminal is a personal computer connected to a network

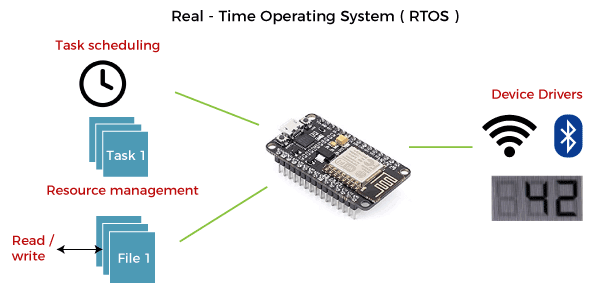
An Operating System which gives the output in real time without any observable delays. This is mostly utilized in ATM end points. Also these kind of Operating Systems are installed in scientific devices and small gadgets. These Operating Systems are specifically designed for particular devices.
An operating system capable of allowing several programs to run at the same time
An operating system capable of supporting and utilising more than one computer processor
This is a text-based user interface (UI) used to run programs, manage computer files and interact with the computer. Programs with command-line interfaces are generally easier to automate via scripting. Many software systems implement command-line interfaces for control and operation. This includes programming environments and utility programs.
The components of the CLI display are :
- Command Prompt
- Cursor
- Input/Commands [text you have typed in]
- Output [of your commands and programs]
GUI is an interface that allows users to interact with different electronic devices using icons and other visual indicators. The graphical user interfaces were created because command line interfaces were quite complicated and it was difficult to learn all the commands in it. In today’s times, graphical user interfaces are used in many devices such as mobiles, MP3 players, gaming devices, smartphones etc. Almost all the present day Operating Systems use graphics on their interfaces.
GUI uses 4 components in order to make a friendly environment. These components are abbreviated as WIMP
- Windows
- 🔥 This displays the information on the screen. There are multiple types of windows in a GUI, such as :
- Container window
- Browser window
- Text terminal window
- Child window
- Message window
- Icons
- 🔥 Files, programs, web pages can be represented using a small picture in a graphical user interface
- 🔥 This picture is known as an icon
- 🔥 Using an icon is a fast way to open documents, run programs
- 🔥 Because clicking on them yields instant access
- Menus
- 🔥 This contains a list a choices and it allows users to select one from them
- 🔥 When any option is clicked in a menu bar which is displayed horizontally across the screen then the Pull-Down Menu appears
- 🔥 Context Menu appears only when the user is pressing the right mouse button. When this is done, a menu will appear under the cursor
- Pointer
- 🔥 A symbol such as an arrow which is moved by a pointing device and can be used to select objects
Graphical User Interface makes use of visual elements mostly. These elements define the appearance of the GUI. Some of these are :
- Widgets
- 🔥 Information in an application can be directly read or influences using the graphical control elements. These are also known as Controls
- 🔥 Normally, widgets are used to display lists of similar items, navigate the system using links, tabs etc & manipulating data using check boxes, radio boxes etc
- Tab
- 🔥 This is associated with a view pane. It usually contains a text label or a graphical icon
- 🔥 Tabs are sometimes related to widgets & multiple tabs allow users to switch between different widgets
- 🔥 Tabs are used in Web Browsers & Multiple web pages can be opened in a web browser & users can switch between them using tabs
| CLI vs GUI | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | CLI | GUI |
| Ease of Use | It is comparatively more difficult to understand and use. | It is comparatively easier to understand and use. |
| Memory Consumption | CLI consumes comparatively less memory. | The GUI consumes comparatively more memory. |
| Level of Precision | Higher precision of work can be obtained using CLI. | GUI offers a lower level of precision. |
| Speed | It works at a higher speed as compared to the GUI. | It works at a much slower speed as compared to the CLI. |
| Keyboard and Mouse | Its OS only requires a user’s keyboard. | Its OS requires both keyboard and mouse to work. |
| Modification of Appearance | We cannot change or modify the CLI operating system’s appearance. | We can change or modify the GUI operating system’s appearance. |
| Graphics | No graphs are included in CLI. | Graphics are always used in the GUI. |
| Menus | No menus are provided in CLI. | The GUI OS comes with menus. |
| Display of Information | The information that the user wants to view is displayed in files and plain text. | The information that the user wants to access is presented in various forms, like plain text, images, videos, gifs, videographs, etc. |
| Input of Information | The input is usually entered at the command prompt in CLI. | We can input the data anywhere on the computer screen in the case of GUI. |
| Pointing devices | Pointing devices are not used at all in CLI. | We use pointing devices in the GUI for choosing/selecting the items we want to. |
| Avoiding Errors | No typing errors or spelling mistakes can be avoided by CLI. | The typing errors or spelling mistakes cannot be avoided by the GUI. |
User interface is one of the significant feature in Operating System. The only way that user can make interaction with a computer. This is a main reason for key success of GUI based Operating Systems.
The following points are considered when User Interface is designed for an application :
- This should enable the user to retain this expertise for a longer time
- This should also satisfy the customer based on their needs
- This should save user’s precious time
- The ultimate aim of any product is to satisfy the customer & This is also to satisfy the customer
- This should reduce number of errors committed by the user
Memory management process makes sure that enough memory is allocated for each process and it also makes sure that the memory is freed once a particular process ends.
OS utilizes both Primary & Secondary Memories efficiently in order to manage the memory for various processes.
The objective of Memory Management process is to improve both the utilization of the CPU and the speed of the computer’s response to its users via main memory.
Process management is function that includes creating and deleting processes(program) & providing mechanisms for processes to communicate and synchronize with each other.
We can call a running computer program or part of the program as a process. All the activities in a computer run as either a single process or a multiple processes.
A computer consists of a collection of processes. All these processes can potentially execute concurrently on a single CPU. They are classified as 2 categories :
- 1. Operating System processes
- 🔥 which is executed by system code
- 2. User Processes
- 🔥 which is execute by user code
The following algorithms are mainly used to allocate the job [process] to the processor.
- FIFO (First In First Out) Scheduling
- 🔥 This algorithm is based on queuing technique.
- 🔥 Technically, the process that enters the queue first is executed first by the CPU, followed by the next and so on.
- 🔥 The processes are executed in the order of the queue (row).
- SJF (Shortest Job First) Scheduling
- 🔥 This algorithm works based on the size of the job being executed by the CPU.
- Round Robin Scheduling
- 🔥 This algorithm is designed especially for time sharing systems.
- 🔥 Jobs (processes) are assigned and processor time in a circular method.
- Based On Priority
- 🔥 The given job (process) is assigned based on a Priority.
- 🔥 The job which has higher priority is more important than other jobs.
MULTI-PROCESSING


TIME-SHARING
File management is an important function of OS which handles the data storage techniques. The operating System manages the files, folders and directory systems on a computer.
File and folder management includes handling file properties, file operations, file access and file systems.
The FAT(File Allocation Table) stores general information about files like filename, type (text or binary), size, starting address and access mode. The file manager of the operating system helps to create, edit, copy, allocate memory to the files and also updates the FAT.
There are few other file management techniques available like Next Generation File System (NTFS) and ext2(Linux).
Some of the services performed by the Operating System in file management are listed below :

DISTRIBUTED OS
- A user at one location can make use of all the resources available at another location over the network.
- Many computer resources can be added easily in the network
- Improves the interaction with the customers and clients.
- Reduces the load on the host computer.
The operating system is responsible for the management of several peripheral devices connected to a computer system.
Device controllers are used to control the peripheral devices whereas Device drivers are used to control software components.
PLUG & PLAY
Today there are devices which work once they are connected [plug & play].
The relevant device drivers are installed automatically once the device is connected to the computer for the first time.
When it does not install automatically you need to manually install it.

The Operating System provides 3 levels of securities to the user end. They are :
- File access level
- 🔥 In order to access the files created by other people, you should have the access permission. Permissions can either be granted by the creator of the file or by the administrator of the system.
- System level
- 🔥 System level security is offered by the password in a multi-user environment.
- Network level
- 🔥 Network security is an indefinable one. So people from all over the world try to provide such a security.
Operating Systems support different types of network connectivities. They support wired and wireless connectivity for hardware devices in the system such as computers, printers, scanners that exist in the network.
- The Operating System also helps in accessing one computer from a remote computer.
- A computer network facilitates from simple text communication to a multimedia data communication.
- Today data communication is utilized at a greater scale in networks.
- This concept is well demonstrated by Cloud Computing.
The Operating Systems should be robust. When there is a fault, the Operating System should not crash, instead the Operating System have fault tolerance capabilities and retain the existing state of system.











/Hanthana_Linux_(operating_system)-Logo.wine.png)