Growth in the computer industry is determined by the development in technology.
Based on various stages of development, computers can be categroised into different generations.
| Generation | Period | Main Component used | Merits/Demerits | Examples |
| First Generation | 1940-1956 |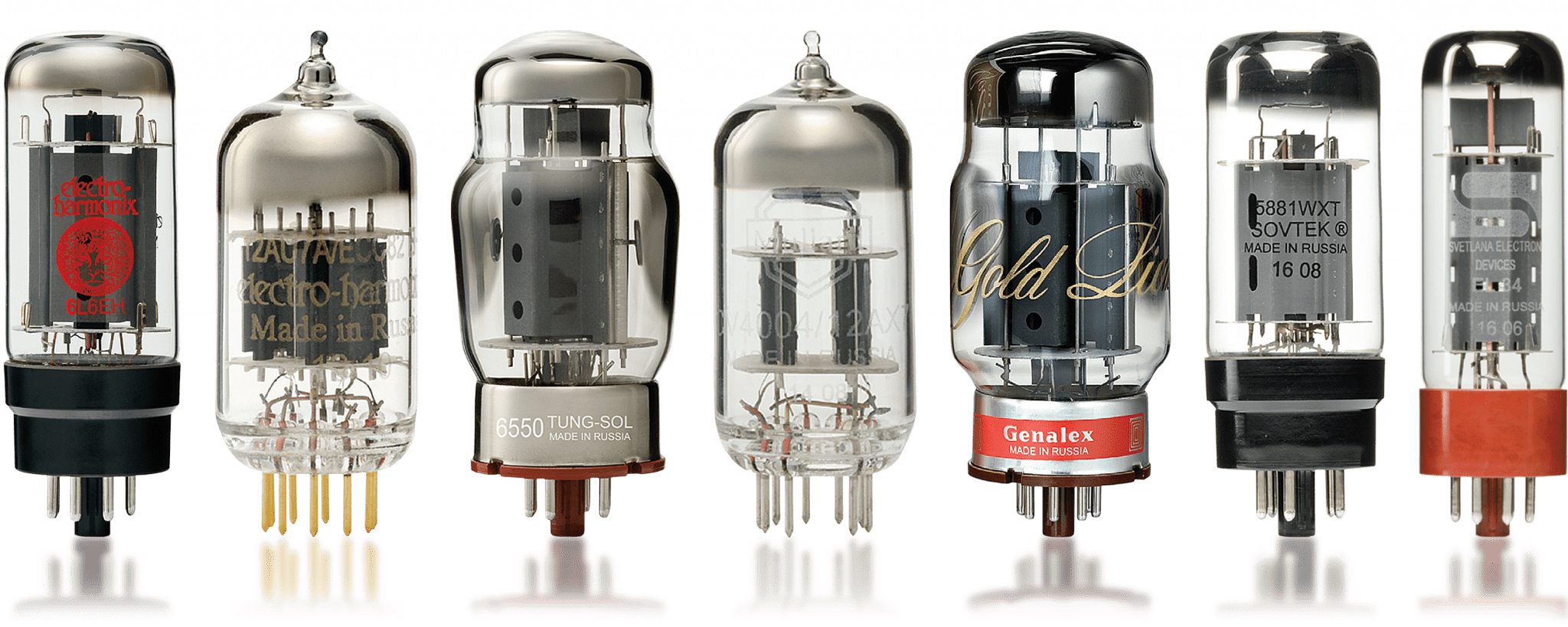  |
|
a) ENIAC b) EDVAC c) EDSAC d) UNIVAC-1 e) IBM-701 |
| Second Generation | 1956-1964 |  |
|
a) IBM-1401 b) IBM-1620 c) IBM-7030 d) UNIVAC-1108 e) UNIVAC-LARC f) Honeywell-400 g) CDC-1604 |
| Third Generation | 1964-1971 |  |
|
a) IBM-360 b) IBM-370 c) PDP-8 d) PDP-11 e) CDC-6600 |
| Fourth Generation | 1971-1980 |
|
a) IBM-PC b) Apple-II |
|
| Fifth Generation | 1980-till date |  |
|
a) IBM-Notebooks b) Pentium-PCs c) SUN-Workstations |
| Sixth Generation | In future |  |
|

FIRST DIGITAL COMPUTER
The ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator) was invented by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly at the University of Pennsylvania and began construction in 1943 and was not completed until 1946.
It occupied about 1,800 square feet and used about 18,000 vacuum tubes, weighing almost 50 tons.
ENIAC was the first digital computer because it was fully functional.
Sixth Generation Computing

Optical Character Recognition (Optical Grapheme Recognition) engine for the Indus Scripts has been developed using Deep Learning Neural Networks (a sub-field of Artificial Intelligence).
TGiven photographs, scans, or any image feed of an Indus Valley Civilization artifact, the system will be able to recognise the inscriptions (the symbol/grapheme sequences) from the image.
There are totally 417 Symbols/ Graphemes/Characters in the Indus Scripts and just 3700+ text inscriptions of data for the machine to learn and attain expert-level status.








